ARG10111
anti-HLA G antibody [G233]
anti-HLA G antibody [G233] for ELISA,Flow cytometry,Immunoprecipitation and Human
Immune System antibody
概述
| 产品描述 | Mouse Monoclonal antibody [G233] recognizes HLA G |
|---|---|
| 反应物种 | Hu |
| 应用 | ELISA, FACS, IP |
| 特异性 | The clone G233 recognizes several isoforms of HLA-G expressed in all populations of extravillous trophoblast (cell columns, interstitial trophoblast, endovascular trophoblast, placental bed giant cells). HLA-G belongs to the nonclassical MHC Class I molecules (MHC Class Ib). G233 has been found not to cross-react with any other MHC Class I antigens (HLA-A, -B, -C, -E, -F). |
| 宿主 | Mouse |
| 克隆 | Monoclonal |
| 克隆号 | G233 |
| 同位型 | IgG2a |
| 靶点名称 | HLA G |
| 抗原物种 | Human |
| 抗原 | HLA-A2.1/human beta2-microglobulin double transgenic mice were immunized with murine L cells transfected with both human beta2-microglobulin and HLA-G. |
| 偶联标记 | Un-conjugated |
| 別名 | HLA G antigen; MHC class I antigen G; HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain G; MHC-G |
应用说明
| 应用建议 |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 应用说明 | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
属性
| 形式 | Liquid |
|---|---|
| 纯化 | Purified from hybridoma culture supernatant by protein-A affinity chromatography. |
| 纯度 | > 95% (by SDS-PAGE) |
| 缓冲液 | PBS (pH 7.4) and 15 mM Sodium azide |
| 抗菌剂 | 15 mM Sodium azide |
| 浓度 | 1 mg/ml |
| 存放说明 | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C or below. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| 注意事项 | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
生物信息
| 数据库连接 |
Swiss-port # P17693 Human HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain G |
|---|---|
| 基因名称 | HLA-G |
| 全名 | major histocompatibility complex, class I, G |
| 背景介绍 | HLA-G belongs to the HLA class I heavy chain paralogues. This class I molecule is a heterodimer consisting of a heavy chain and a light chain (beta-2 microglobulin). The heavy chain is anchored in the membrane. HLA-G is expressed on fetal derived placental cells. The heavy chain is approximately 45 kDa and its gene contains 8 exons. Exon one encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the alpha1 and alpha2 domain, which both bind the peptide, exon 4 encodes the alpha3 domain, exon 5 encodes the transmembrane region, and exon 6 encodes the cytoplasmic tail. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| 生物功能 | Involved in the presentation of foreign antigens to the immune system. Plays a role in maternal tolerance of the fetus by mediating protection from the deleterious effects of natural killer cells, cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, macrophages and mononuclear cells. [UniProt] |
| 研究领域 | Immune System antibody |
| 预测分子量 | 38 kDa |
检测图片 (2) Click the Picture to Zoom In
-
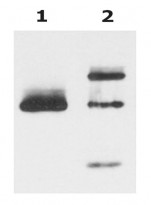
ARG10111 anti-HLA G antibody [G233] IP image
Immunoprecipitation: HLA-G from HLA-G1 transfectants (LCL-HLA-G1) immunoprecipitated by ARG10106 anti-HLA G antibody [MEM-G/9] and protein G. HLA-G was stained with ARG10111 anti-HLA G antibody [G233] in cell lysate (Lane 1) and in the immunoprecipitate (Lane 2).
-
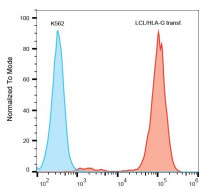
ARG10111 anti-HLA G antibody [G233] FACS image
Flow Cytometry: HLA-G transfectants stained with ARG10111 anti-HLA G antibody [G233], followed by APC-conjugated Goat anti-Mouse antibody.
克隆号文献