ARG65808
anti-TNFAIP3 / A20 antibody
anti-TNFAIP3 / A20 antibody for ICC/IF,IHC-Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections,Western blot and Human,Mouse,Rat
概述
| 产品描述 | Rabbit Polyclonal antibody recognizes TNFAIP3 / A20 |
|---|---|
| 反应物种 | Hu, Ms, Rat |
| 应用 | ICC/IF, IHC-P, WB |
| 宿主 | Rabbit |
| 克隆 | Polyclonal |
| 同位型 | IgG |
| 靶点名称 | TNFAIP3 / A20 |
| 抗原物种 | Human |
| 抗原 | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide around the center region of Human A20. |
| 偶联标记 | Un-conjugated |
| 別名 | A20; OTUD7C; EC 6.3.2.-; Zinc finger protein A20; Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3; Putative DNA-binding protein A20; TNFA1P2; OTU domain-containing protein 7C; TNF alpha-induced protein 3; EC 3.4.19.12 |
应用说明
| 应用建议 |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 应用说明 | IHC-P: Antigen Retrieval: Boil tissue sections in Sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0) * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
属性
| 形式 | Liquid |
|---|---|
| 纯化 | Affinity purification with immunogen. |
| 缓冲液 | Liquid (pH 7.3), 0.42% Potassium phosphate, 0.87% NaCl, 0.01% Sodium azide and 30% Glycerol. |
| 抗菌剂 | 0.01% Sodium azide |
| 稳定剂 | 30% Glycerol |
| 存放说明 | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| 注意事项 | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
生物信息
| 数据库连接 |
Swiss-port # P21580 Human Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 Swiss-port # Q60769 Mouse Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 |
|---|---|
| 基因名称 | TNFAIP3 |
| 全名 | tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 |
| 背景介绍 | This gene was identified as a gene whose expression is rapidly induced by the tumor necrosis factor (TNF). The protein encoded by this gene is a zinc finger protein and ubiqitin-editing enzyme, and has been shown to inhibit NF-kappa B activation as well as TNF-mediated apoptosis. The encoded protein, which has both ubiquitin ligase and deubiquitinase activities, is involved in the cytokine-mediated immune and inflammatory responses. Several transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012] |
| 生物功能 | Ubiquitin-editing enzyme that contains both ubiquitin ligase and deubiquitinase activities. Involved in immune and inflammatory responses signaled by cytokines, such as TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta, or pathogens via Toll-like receptors (TLRs) through terminating NF-kappa-B activity. Essential component of a ubiquitin-editing protein complex, comprising also RNF11, ITCH and TAX1BP1, that ensures the transient nature of inflammatory signaling pathways. In cooperation with TAX1BP1 promotes disassembly of E2-E3 ubiquitin protein ligase complexes in IL-1R and TNFR-1 pathways; affected are at least E3 ligases TRAF6, TRAF2 and BIRC2, and E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UBE2N and UBE2D3. In cooperation with TAX1BP1 promotes ubiquitination of UBE2N and proteasomal degradation of UBE2N and UBE2D3. Upon TNF stimulation, deubiquitinates 'Lys-63'-polyubiquitin chains on RIPK1 and catalyzes the formation of 'Lys-48'-polyubiquitin chains. This leads to RIPK1 proteasomal degradation and consequently termination of the TNF- or LPS-mediated activation of NF-kappa-B. Deubiquitinates TRAF6 probably acting on 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin. Upon T-cell receptor (TCR)-mediated T-cell activation, deubiquitinates 'Lys-63'-polyubiquitin chains on MALT1 thereby mediating disassociation of the CBM (CARD11:BCL10:MALT1) and IKK complexes and preventing sustained IKK activation. Deubiquitinates NEMO/IKBKG; the function is facilitated by TNIP1 and leads to inhibition of NF-kappa-B activation. Upon stimulation by bacterial peptidoglycans, probably deubiquitinates RIPK2. Can also inhibit I-kappa-B-kinase (IKK) through a non-catalytic mechanism which involves polyubiquitin; polyubiquitin promotes association with IKBKG and prevents IKK MAP3K7-mediated phosphorylation. Targets TRAF2 for lysosomal degradation. In vitro able to deubiquitinate 'Lys-11'-, 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63' polyubiquitin chains. Inhibitor of programmed cell death. Has a role in the function of the lymphoid system. Required for LPS-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines and IFN beta in LPS-tolerized macrophages. [UniProt] |
| 预测分子量 | 90 kDa |
| 翻译后修饰 | Proteolytically cleaved by MALT1 upon TCR stimulation; disrupts NF-kappa-B inhibitory function and results in increased IL-2 production. It is proposed that only a fraction of TNFAIP3 colocalized with TCR and CBM complex is cleaved, leaving the main TNFAIP3 pool intact. |
检测图片 (3) Click the Picture to Zoom In
-
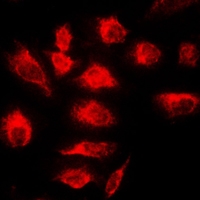
ARG65808 anti-TNFAIP3 / A20 antibody ICC/IF image
Immunofluorescence: Formalin-fixed HeLa cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 5-10 min and blocked with 3% BSA-PBS for 30 min at RT. Cells were stained with ARG65808 anti-TNFAIP3 / A20 antibody in 3% BSA-PBS and incubated overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Cells were washed with PBST and incubated with a DyLight 594-conjugated secondary antibody (red) in PBS at RT in the dark. DAPI was used to stain the cell nuclei (blue).
-
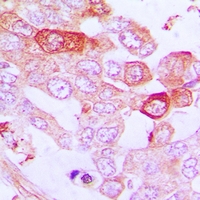
ARG65808 anti-TNFAIP3 / A20 antibody IHC-P image
Immunohistochemistry: Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded Human lung cancer. Antigen retrieval: Boil tissue sections in Sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0). The section was then incubated with ARG65808 anti-TNFAIP3 / A20 antibody at RT and detected using an HRP conjugated compact polymer system. DAB was used as the chromogen. The section was then counterstained with haematoxylin and mounted with DPX.
-
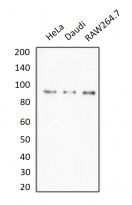
ARG65808 anti-TNFAIP3 / A20 antibody WB image
Western blot: HeLa, Daudi and RAW264.7 whole cell lysates stained with ARG65808 anti-TNFAIP3 / A20 antibody.